Categories
- » Accessories
- » Cloning & Propagation
- » Controllers
- » Ducts, Pipes, Clamps
- » Fans
- » Filters
- » Grow Media
- » Grow Systems
- » FloraFlex
- » Indicators & Monitors
- » Method Seven
- » Lighting
- » Nutrients & Pest Control
- » Pots & Trays
- » Pumps
- » Tents, Plastics & Foils
- » All Products
- » Seeds & Clones
- » Black Friday


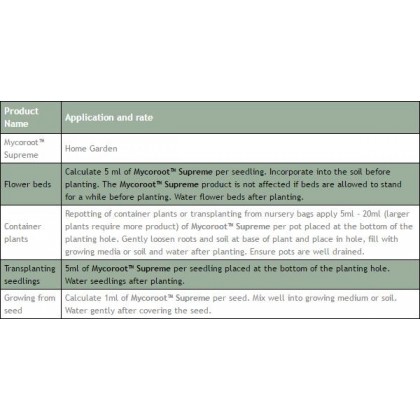
MycoRoot 214g
BENEFITS:
Increased uptake of nutrients and water.
Increased soil biological activity.
Improved soil structure and aeration.
Reduced effects from drought.
Reduced effects from root pathogens.
Reduced chemical inputs and environmental damage.
WHAT ARE MYCORRHIZAL FUNGI?
Mycorrhiza literally means “fungus root”.
These are beneficial fungi found in undisturbed soils.
These fungi form a symbiotic relationship with 90% of all plant roots.
The host plant receives mineral nutrients from the fungus.
The fungus obtains sugars from the host plant.
There are several types of mycorrhizal associations.
The most commonly encountered are the arbuscular mycorrhizal (AM) fungi.
HOW DO THEY FUNCTION?
The fungus grows by means of fungal filaments called hyphae.
The filaments grow inside and outside of the roots.
The fungus is intimately associated with the plant roots, providing a link between the soil and the plant.
They extend the plant rooting system improving root functions.
They allow for better exploitation of the soil environment.
They increase the surface area available for nutrient uptake.
They make nutrients soluble which are normally not accessible to roots.
They influence the soil environment covered by the fungal filaments.
Encourages growth of beneficial bacteria and other non-disease causing fungi.
They ward off unwanted organisms which can cause plants diseases.
They produce a biological glue that promotes soil stability and increases moisture penetration and aeration of the soil.
Customers who bought this product also bought:
Customer ratings and reviews


















